Bad breath (Halitosis), – is the unpleasant odor emitted from the mouth. This is an embarrassing condition wherein some people aren’t aware of. This is the result of proteins breakdown by bacteria.
Causes of Bad Breath
- Poor oral hygiene
- Tooth decay
- Dry mouth (Xerostomia)
- Gum disease
- Metals in the mouth
- Tooth infection
Medical Conditions
- Local infection in the respiratory tract
- Chronic sinusitis
- Postnasal drip
- Chronic bronchitis
- Diabetes
- Gastrointestinal disturbance
- Liver or kidney ailment
- Disorder in metabolism
- Fasting
Treatment of bad breath
- Maintaining of good oral health
- Regular dental check-up
- Avoid foods that have offensive smell after eating such garlic & onions and spicy food.
- Refrain from smoking
- Treatment of systemic diseases and local infection in the respiratory tract
- Treat dry mouth
- Proper nutrition
- Avoid too much coffee and alcohol
- Drink plenty of water
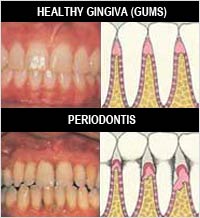
Gum Disease is an infection of the gums which is caused by a film of bacteria that coats everyone’s teeth. It can occur at any age, but it is most common among adults. In the early reversible stage of gum disease, called gingivitis, gums can become red, swollen and bleed easily. When the disease progresses to the bone, which supports the teeth, it is called periodontitis and at that point can cause irreversible damage. In the advanced stages of the disease, the bone and soft tissues which support the teeth are destroyed and this may cause the teeth to become loose, fall out, or have to be removed by a dentist.
Causes of Gum Disease
Treatment of gum disease
Once the bacteria and toxins that irritate the tissue are eliminated, the gum can often reattach to the tooth. If gum disease is caught in the early stages, professional cleaning, combined with good oral hygiene and diet, is often enough to restore oral health.
In the more advanced stages of gum disease, a variety of treatment techniques may be necessary. These can include gum surgery to remove tartar from deep pockets and to regenerate lost gum and bone. Depending on the situation, bite adjustment, bridgework, dental implants and orthodontics may also be recommended. Treatment depends and is tailored of the individual’s concern.
Interested to know more about the service?
Schedule a visit now!



