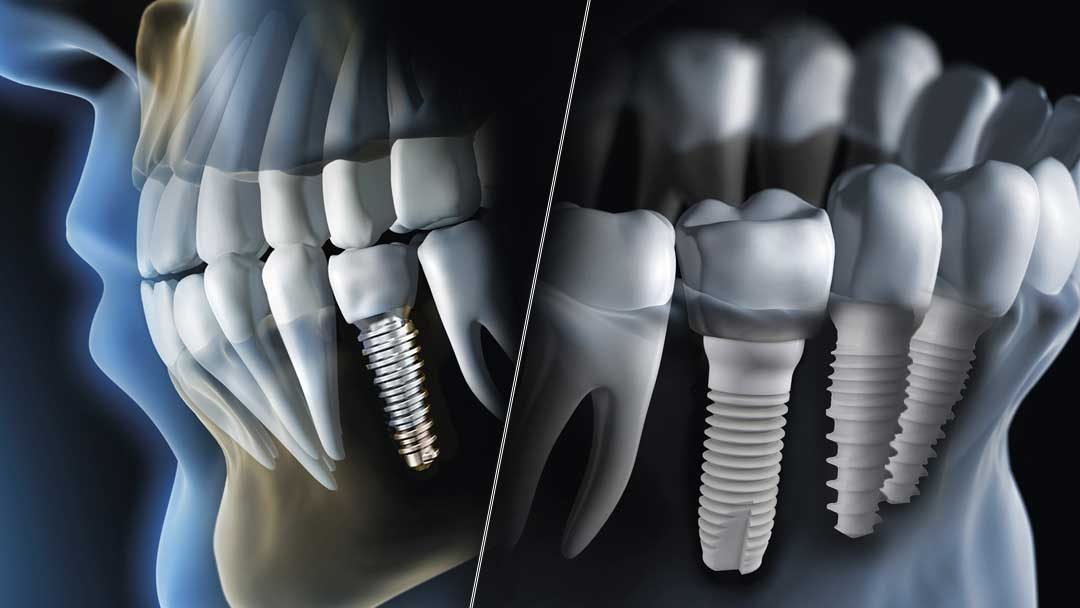
What are Dental implants?, – Dental implants are small, sturdy, titanium or zirconia (ceramic) implant post that acts as the root structure in replacement of a natural root of the tooth. A dental implant is placed into a patient’s upper or lower jaw bone. After the bone has grown around the implant, implants can hold a crown, bridge or overdenture just like roots hold natural teeth in place.
Implants are the latest dental technology for replacing the roots of lost teeth. They are used to support crowns, bridges, and dentures. Implants offer stability, comfort and a sense of freedom for those who have missing teeth and want to regain their smile back.
Indications for Dental Implants
Loss of Prosterior
Loss of Individual Teeth
Total Loss of Teeth
Denture users suffer from gum pain, lack of denture, stability, discomfort and reduced chewing capability. Implants can provide stability and retention for dentures by means of connectors assembled on the implants.
b) Fixed Full Mouth Bridgework
Placement of a large number of implants can provide an adequate base for full fixed reconstruction of the teeth.
Non-metal (Ceramic) Zirconium Implant
The microstructure surface in the bone promotes osseointegration and supports long-term success of the implant restoration.

– The soft tissue adapts perfectly to the implant. Plaque accumulation is avoided and hence the risk of perioimplantitis is reduced. The root-shaped implant body with self-cutting cylindrical double thread condensates the bone during the insertion process and creates outstanding primary stability. The conically rounded apex simplifies the intergration and protects the bone structure.
Interested to know more about the service?
Schedule a visit now!